App Permission IVT Risk Assessment For the Android Mobile Ecosystem
INTRODUCTION
What is an app permission?
An app permission is a mechanism for controlling access to a system- or device-level function through the device’s operating system. Permissions usually can have privacy implications (e.g. access to fine-grained location). App permissions help support user privacy by protecting access to the following [1]:
-
Restricted data, such as system state and a user's contact information.
-
Restricted actions, such as connecting to a paired device and recording audio.
What are the various types of permissions?
An Android app that needs to access sensitive data or functionality needs to specify the permissions it will need in the app manifest file (a file containing configuration information). The list of recognized permissions by the Android Operating System (OS) are outlined in [2]. Google has classified each permission according to its security level and its associated privacy risk. There are also custom permissions that a developer can define that are not included in the official Google manifest; however, these are not going to be the focus of our analysis.
Typical vs atypical permissions and the risks for IVT
Permissions are needed for providing certain functionalities to mobile apps. For example, apps such as Google Maps need access to fine-grained GPS information in order to navigate the user to a given destination. However, a drawing app does not necessarily need fine-grained location data in order to operate. Motivated by this, permissions can be further classified as typical and atypical, depending on if they are needed in order to provide the services that an app is intended for.
Typical and Atypical permissions can usually be identified using the app category (or genre) as a proxy, since the most common permissions are usually present for all the apps of a given category. On the other hand, atypical permissions pose additional risk to end users due to the fact that more permissions are given than are required, thus making them perfect avenues for generating IVT or conducting other malicious activities. In the sections below, we analyze the IVT risk scores associated with each permission that an app asks for in order to assess how likely a given permission is to be abused.
IVT Permission Risk Assessment
What is Pixalate’s approach for IVT permission risk assessment?
Pixalate assesses each app permission in terms of the likelihood to be used for generating IVT. To do so, Pixalate detects permissions that correlate with higher IVT compared to the average IVT of a given app category. For example, within the list of navigation apps, the presence of location permission does not increase the odds of seeing higher IVT than usual in the category, since the permission is used by all the apps in the category. However, the presence of location permission in the category “games” (as an example) can be found to be associated with the app having higher IVT rates. Thus, we can flag the location permission in such cases as high risk.
Using the method described above, apps can be essentially evaluated in terms of the following criteria:
-
Is the permission requested within an app needed for functionality?
-
Can this permission be an indicator that this app is exhibiting behavior that increases IVT?
-
Overall, does the app request a high number of unnecessary permissions?
Correlation vs Causation
It is important to note here that Pixalate’s IVT permission risk assessment does not imply “causation.” Instead, it really measures “correlation.” What this means is that the presence of a given permission makes it more likely for the app to generate high rates of IVT, without necessarily implying that this permission is the one “causing” the IVT by itself, since more complex methods can be used (e.g. using multiple permissions in conjunction) to generate IVT.
IVT Permission Risk Methodology
How does Pixalate evaluate permissions in terms of their relationship to IVT?
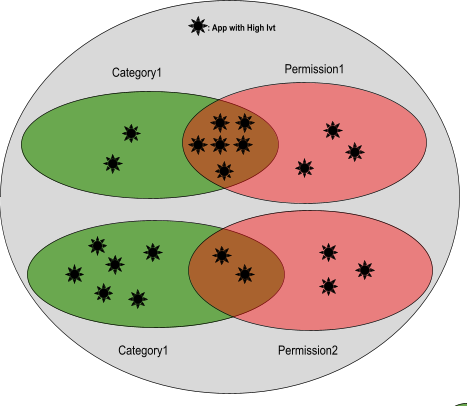
Figure 1. Example of permission-level app classification for a given category.
Phase 1: Category level permission scoring
-
Initially, all the apps are classified as high or low risk according to their IVT levels.
-
Then, the ratio of high risk apps within each category is calculated.
-
Then we calculate how many high risk apps in that category are within a certain permission.
-
Then we assess how often a permission has high risk apps within a category compared to how often that category has high risk apps.
-
If the ratio of apps within a permission & category is above the ratio for the whole category, then we associate a risk score to the permission (at the category level) that is proportionate to ratio of the two.
Phase 2: App-level permission Scoring
Because an app can have many IVT risky permissions, we calculate an overall IVT permission score for the app as follows:
-
We count how many high- and medium-risk permissions exist normally in a given category, and we compare how many of those high- and medium-risk permissions exist for an app in the category.
-
We then compare the app-level ratio with the category-level, and then rank High, Medium, Low depending on the magnitude of this ratio.
Caveats
-
If there are not enough apps (less than 10) within a category, we then fall back to the high risk app ratio of the permission across all categories.
-
We separately create a high/medium/low risk for if a permission overall is high risk compared to other permissions.
-
If a permission appears in less than 10 apps, then we do not rank the permission at all and defaults to low.
-
There are permissions that we automatically flag as high IVT risk based on historical IVT data. The full list of such permissions is shown in the table below.
Default IVT Risk Permissions:
|
Permission |
Description |
Permission Risk Assessment |
High IVT Risk Permission |
|
ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION |
Allows an app to access location in the background. |
Dangerous |
TRUE |
|
WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE |
Allows an application to write to external storage. |
Dangerous |
TRUE |
|
WAKE_LOCK |
Allows using PowerManager WakeLocks to keep processor from sleeping or screen from dimming. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED |
Allows an application to receive the Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED that is broadcast after the system finishes booting. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND |
Allows a companion app to run in the background. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND |
Allows a companion app to use data in the background. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
DISABLE_KEYGUARD |
Allows applications to disable the keyguard if it is not secure. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW |
Allows an app to create windows using the typeWindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY, shown on top of all other apps. |
SIgnature |
TRUE |
|
UNINSTALL_SHORTCUT |
Allows application to uninstall shortcut to the app |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
GET_ACCOUNTS |
Allows access to the list of accounts in the Accounts Service. |
Dangerous |
TRUE |
|
READ_PHONE_STATE |
Allows read only access to phone state, including the phone number of the device, current cellular network information, the status of any ongoing calls, and a list of any PhoneAccounts registered on the device. |
Dangerous |
TRUE |
|
WRITE_SYNC_SETTINGS |
Allows applications to write the sync settings. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES |
Allows an application to request deleting packages. |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
KILL_BACKGROUND_PROCESSES |
Allows an application to call ActivityManager.killBackgroundProcesses(String). |
Normal |
TRUE |
|
WRITE_SETTINGS |
Allows an application to read or write the system settings. |
SIgnature |
TRUE |
|
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES |
Allows an application to request installing packages. |
SIgnature |
TRUE |
|
REBOOT |
Required to be able to reboot the device. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
READ_LOGS |
Allows an application to read the low-level system log files. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
DIAGNOSTIC |
Allows applications to RW to diagnostic resources. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
FACTORY_TEST |
Run as a manufacturer test application, running as the root user. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
INSTALL_PACKAGES |
Allows an application to install packages. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
PACKAGE_USAGE_STATS |
Allows an application to collect component usage statistics |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
UPDATE_DEVICE_STATS |
Allows an application to update device statistics. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
WRITE_SECURE_SETTINGS |
Allows an application to read or write the secure system settings. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
MOUNT_FORMAT_FILESYSTEMS |
Allows formatting file systems for removable storage. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
ACCESS_CHECKIN_PROPERTIES |
Allows read/write access to the "properties" table in the checkin database, to change values that get uploaded. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
BROADCAST_PACKAGE_REMOVED |
Allows an application to broadcast a notification that an application package has been removed. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
INSTALL_LOCATION_PROVIDER |
Allows an application to install a location provider into the Location Manager. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
|
MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS |
Allows mounting and unmounting file systems for removable storage. |
Not for use by third-party applications |
TRUE |
References
[1] [Online] Permissions on Android: https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/permissions/overview
[2] [Online] App Manifest Permissions: https://developer.android.com/reference/android/Manifest.permission
This information: (i) is confidential and copyright Pixalate, Inc., with all rights reserved, and (ii) may not be redistributed or published in any manner, in whole or in part, without the prior express written permission of Pixalate, Inc.
© 2021 Pixalate, Inc. | All Rights Reserved
-1.png?width=150&height=60&name=pixalate-full-logo%20(1)-1.png)